|
Five thousand years ago, Egypt was a rich
country because of the River Nile. Around the
river, the farmers grew crops and raised
animals. The Nile was also home to lots of fish,
birds and wild animals which people hunted
for food and sport. Travelling by land was
difficult in the hills and deserts of ancient
Egypt, so people travelled by boats.
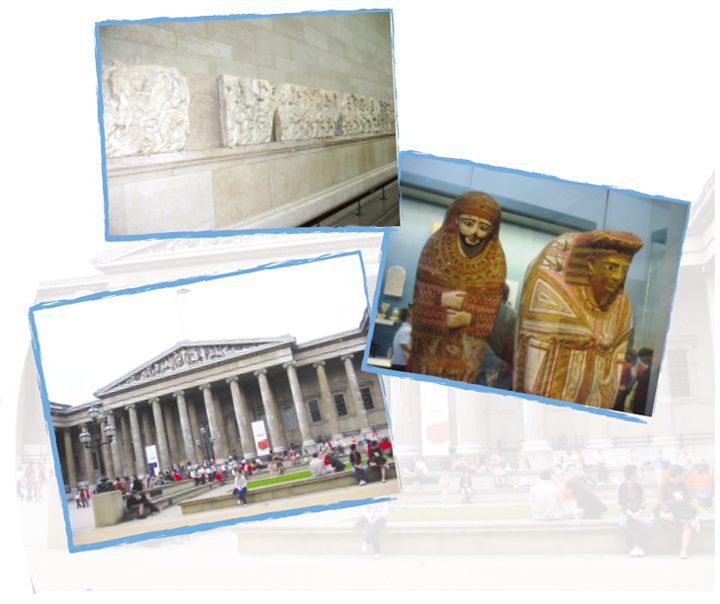
The ancient Egyptian pharaohs built temples
and put up huge stone statues. Rameses II was
the pharaoh who ruled for sixty-seven years
and put up more statues of himself than any
other pharaoh.
The ancient Egyptians believed in life after
death. That's why they became very good at
mummification. Nowadays, with modern
technology, we can look inside mummies.
There are lots of them in the British Museum.
adapted from ‘The World of the British Museum' - C. Whitaker, 2000;
London: British Museum Press
|
2 |
Read the text more carefully to
complete David's notes. |
- A lot of farming around the
1 .................................
- People hunted for 2 ..................
and sport.
- People travelled by 3.....................
- Rameses II ruled for 4 ...........
years.
- 5 ..................................was an
Egyptian technique.
- Modern technology helps us
- 6 ..........................................
3 |
Check your answers with
another Student A. |
4 |
Pair up with a Student B.
Turn to page 146 to do the
Speaking task. |
|